Verité Research and the World Bank developed a methodology to monitor online proactive disclosure of information, in accordance with the RTI Act. Verité Research then used this methodology to monitor and evaluate the online proactive disclosure of information across 55 public authorities in Sri Lanka. The report found that 20% of public authorities scored in the ‘moderately satisfactory’ band. The majority, 75% of public authorities scored within the ‘moderately unsatisfactory’ band and 5% scored ‘unsatisfactory’. No authority scored ‘satisfactory’ or ‘highly satisfactory’.
Export promotion has been a key policy objective of successive governments of Sri Lanka. The Government aims to double the value of exports to USD 20 billion by 2020. Currently, the government is taking measures to improve the investment climate and ease the bureaucratic burden for the private sector; investors and businesses. One such bureaucratic hindrance is the export registration process. This policy note finds that although the current registration process was introduced with the intention of identifying and supporting new exporters, its execution severely impedes the achievement of this goal.
අපනයනය කරන්නට සිතන ව්යාපාරිකයන් අපනයනකරුවෙකු ලෙස ලියාපදිංචි වීම ලංකාවේ නීතිය යටතේ අනිවාර්ය වේ. ඒක පුද්ගල සහ හවුල් ව්යාපාරිකයන්ට අදාළ ලියාපදිංචි වීමේ ක්රියාවලිය අනවශ්ය ලෙස දීර්ඝ, අකාර්යක්ෂම සහ දුෂ්කර එකක් බව වෙරිටේ පර්යේෂණ ආයතනය කල අධ්යනයකින් හෙළි දරවු විය. වත්මන් ක්රියාවලිය අවම වශයෙන් පියවර 10කින් සමන්විත වන අතර, විවධ රාජ්ය ආයතන 6ක් ඊට සම්බන්ධ වේ. මේ සඳහා සති 1-3ක කාලයක් ගත විය හැක. අපනයන බලපත්ර අවැසි භාණ්ඩ අපනයනය කරන්නට සිතන ව්යාපාරිකයන්ට සිය ලියාපන්දිචිය සම්පුර්ණ කිරීමට මීට අමතරව තවත් සති කිහිපයක් වැය කරන්නට සිදු වේ. නව අපනයනකරුවන් හඳුනා ගෙන ඔවුනට අත්වැලක් සැපයීමේ අරමුණින් හඳුන්වා දී ඇති මෙම අනිවාර්ය ලියාපදිංචිය, ක්රියාත්මක වී ඇත්තේ එම අරමුණට පටහැනි ආකාරයෙනි. දේශීය ව්යාපාරිකයන් අපනයනය සඳහා දිරි ගැන්වීමට නම් මෙම ක්රියාවලිය සරල, කෙටි සහ තර්කාන්විත එකක් බවට පත් කිරීම ඉතා වැදගත්ය.
Despite an increasing number of natural disasters in recent years, Sri Lanka suffers from a limited uptake of natural disaster insurance coverage. Sri Lanka’s small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are especially vulnerable to the impact of such disasters. While there are many factors that contribute to the limited use of natural disaster insurance in Sri Lanka, our policy note identifies the lack of accessible information, especially in the vernacular, to be one of the primary causes. Our findings revealed that information on natural disaster insurance is provided almost exclusively in English by private insurance companies as well as state provided welfare schemes. Given that the areas affected by natural disasters outside Colombo have an English literacy rate below 30%, provisions of such information in the vernacular can significantly help SMEs tap into the benefits of natural disaster insurance.
ඉහළ යමින් පවතින ස්වභාවික ආපදාවන් කුඩා හා මධ්ය පරිමාණ ව්යාපාරයන් මුහුණ දෙන විශාල අභියෝගයකි. ආපදා රක්ෂණ ආවරණයන් යනු එවන් ආපදාවන්ගෙන් වූ හානියෙන් පසු සිය ව්යාපාර නැවත ගොඩ නගා ගැනීමට ඇති ප්රයෝජනවත් මෙවලමකි. එහෙත් ලංකාවේ ආපදා රක්ෂනාවරණ අනුපාතය ඉතා පහල මට්ටමක පවතී. මෙම ප්රතිපත්ති සටහන පෙන්වා දෙන්නේ සිංහල සහ දෙමල භාෂාවන්ගෙන් රක්ෂණ ලියවිලි ලබා ගැනීමට නොහැකි වීම, මෙතෙක් හඳුනා නොගත්, රක්ෂනාවරන අනුපාතය පහල අගයක් ගැනීමට හේතු වන වැදගත් හේතුවක් බවයි. ලංකාව සියලූම පොදු සන්නිවේදනයන්; සිංහල, දෙමල සහ ඉංග්රීසි යන මූලික භාෂා ත්රිත්වයෙන්ම සිදු කිරීමේ ප්රතිපත්තියකින් බැඳී සිටිය ද, අපගේ අධ්යයනය මගින් සොයා ගනු ලැබුවේ රක්ෂණ ලියවිලි සහ තොරතුරු සඳහා එකී ප්රතිපත්තිය අදාල කර නොමැති බවය.
There are three false claims that have been prevalent in print media, in relation to the tax and price increases of cigarettes in the last quarter of 2016. The claims were that (i) tax revenue reduced, (ii) beedi consumption increased, and (iii) CTC lost economic value. The Insight provides analysis that contests all three claims.
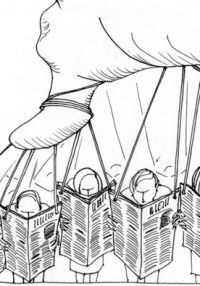
Sri Lanka is a signatory to the International Treaty, Framework Convention on Tobacco Control since 2003. It has not yet implemented the provisions relating to protecting tobacco policy from vested interests. This Insight explores the consequences of not doing so and meaningful steps that can be taken towards mitigating the influence of vested interests.
Analysis of past tax and price data reveals two aspects of cigarette pricing that are hidden from media reporting: first, net-of-tax price grew at a faster rate than the tax per cigarette; second, that the government’s tax share of the cigarette price has fallen over time.
Sri Lanka and China decided to enter into a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) in August 2013 to further expand trade between the two countries. Technical negotiations, which officially commenced in September 2014, are still underway with five rounds of negotiations having been concluded. China is the world’s second largest economy, its largest exporter and its second largest importer. For a small market economy like Sri Lanka, an agreement with a country such as China presents exciting opportunities as well as daunting challenges. This briefing note provides an assessment of the challenges and opportunities that Sri Lanka is likely to face in operating under an FTA with China. Potential challenges and opportunities have been identified by analysing the key features of China’s existing FTAs with other countries.
The Global Competitiveness Index (GCI), ranks the competitiveness of economies. The GCI score is calculated using two types of indicators: objective (or measurable) indicators and sentiment (or subjective) indicators. While Sri Lanka has experienced a steady increase in the objective indicators, the steep decline in sentiment indicators have overshadowed these improvements, driving down the country’s overall score and rank.